∫ e tan x sec 2 x dx = ?If the integral ∫ (5 tan x / tan x − 2)dx = x a ln sin x 2 cos x k Recent Updates Fractions;Use Substitution tan x dx = sin x COs x dx set u = COs x then we find du = sin x dx
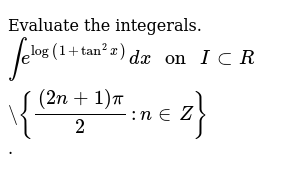
Evaluate The Integerals Br Int E Log 1 Tan 2 X Dx
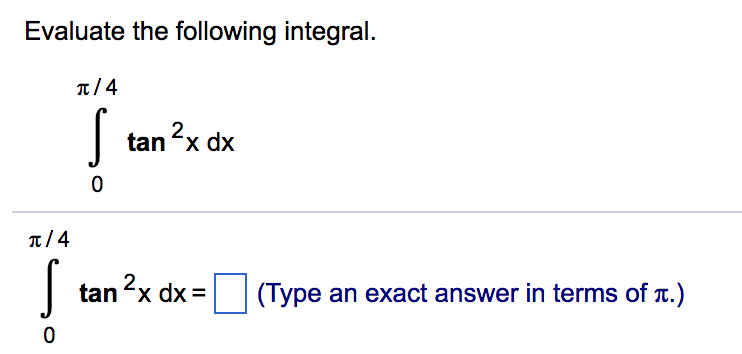
Integral of tan 2 x dx
Integral of tan 2 x dx-Share It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered by Prerna01 (521k points) selected byNew code inspection engine updated to clang version 12 Download Enrico Gregorio




The Integral Intsec 2 X Secx Tanx 9 2 Dx Equals For Some Arbitrary Constant K
Exponents and Square Roots; Integral of u^2 is NOT (u^3)/3 c Rather, integral of (u^2)du = (u^3)/3 c In (tan^2)x your 1st mistake is not writing dx Note that dx is NOT always du!!!!!1 x2 dx= tan 1 x (9) Z 1 a2 x2 dx= 1 a tan 1 x a 1 (10) Z x a2 x2 dx= 1 2 lnja2 x2j (11) Z x2 a 2 x dx= x atan 1 x a (12) Z x3 a 2 x dx= 1 2 x2 1 2 a2 lnja2 x2j (13) Z 1 ax2 bx c dx= 2 p 4ac b2 tan 1 2ax b p 4ac b2 (14) Z 1 (x a)(x b) dx= 1 b a ln a x b x;
Dave's Math Tables Integral tan(x) (Math Calculus Integrals Table Of tan x) Discussion of tan x = lncos x C 1 Proof Strategy Make in terms of sin's and cos's;You can not integrate tan 2 x but you can integrate sec 2 x Since sec 2 x = 1 tan 2 x Then tan 2 x = sec 2 x1 so the intragral of tan 2 x dx = the integral of (sec 2 x1) dx = intrgral of sec 2 x dx integral of 1 dx = tanxx C Answered by Nandini P • Maths tutor 131 Views See similar Maths A Level tutors Need help with Maths?One to one online tuition can be a great way toShare It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered Aug 9 by Vaiga (4k points) selected Sep 2 by Aeny Best answer Correct answer is C Formula Therefore, ← Prev Question Next Question → Find MCQs & Mock Test Free JEE Main
Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integral of sin(x), integ Integrate ∫ tan 3 2x sec 2x dx class12;Integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1sqrt(x)) integrate x/(x1)^3 from 0 to infinity;
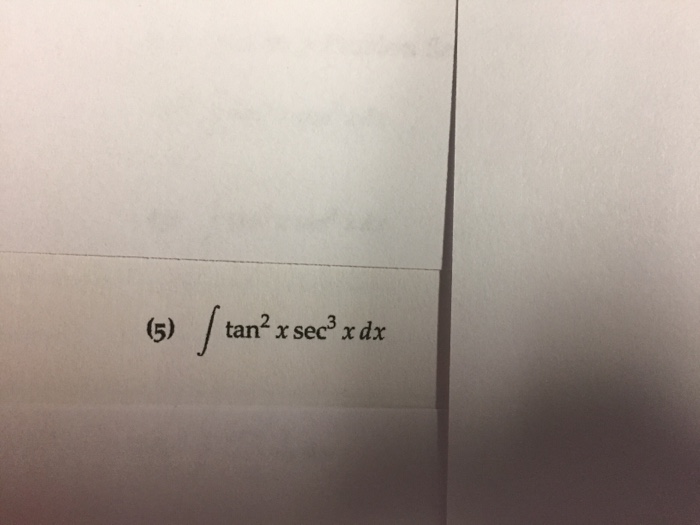



Solved Integral Tan 2x Sec 3 X Dx Chegg Com
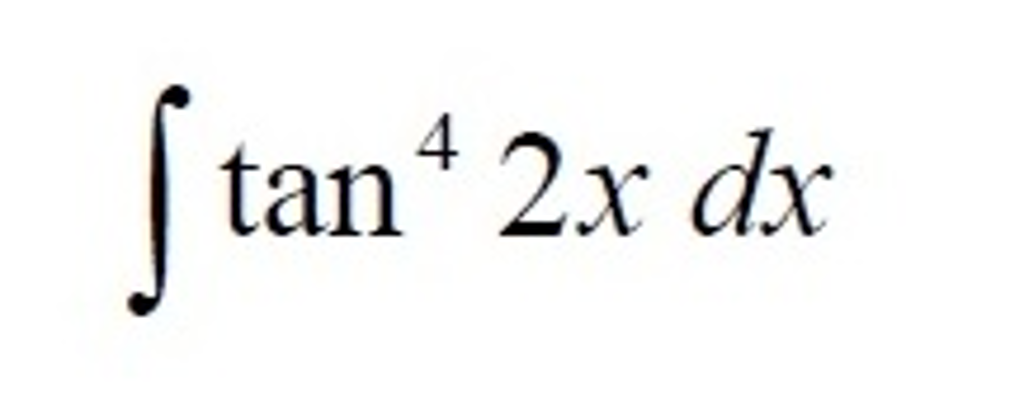



Solved Integral Tan 4 2x Dx Chegg Com
Answer (1 of 5) \displaystyle\int \sin^2\,x \tan\,x\,dx = \displaystyle\int (1 \cos^2\,x) \tan\,x\,dx = \displaystyle\int \tan\,x\,dx \displaystyle\int \cos\,xU = x/2 dx du = 1/2 dx 2du = dx integral of tan u = lnsecu *Dx u C = lnsec(x/2) * 2 C =2 *lnsec(x/2) C 41K views View upvotes 9 8 Rishabh, lives in India (02present) Answered 2 years ago 45K views View upvotes 9 3 Sponsored by Whole Tomato Software Try Visual Assist 213 now!Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!




Integration By Parts Int Tan 2 4x Sec 4x Dx Mathematics Stack Exchange



Math Problems Simplifying With Trigonometry Identities And Then Integration
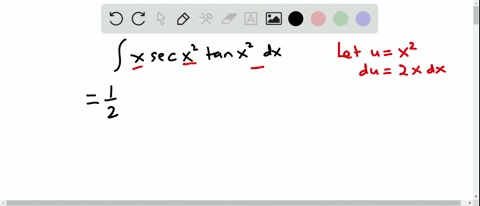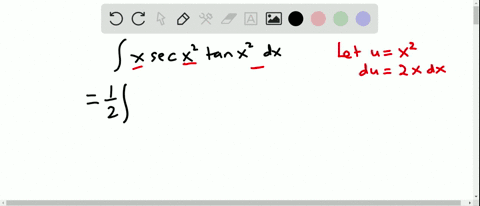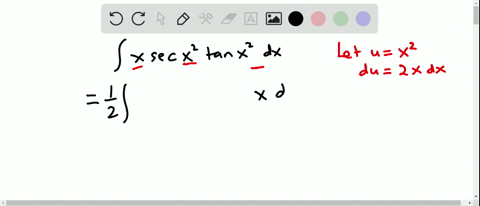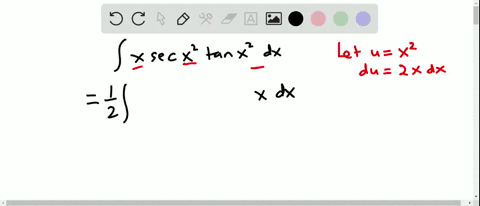
Find the Integral tan (3x) tan (3x) tan ( 3 x) Let u = 3x u = 3 x Then du = 3dx d u = 3 d x, so 1 3du = dx 1 3 d u = d x Rewrite using u u and d d u u Tap for The answer is tanx −x c Remembering that the derivative of y = tanx is y' = 1 tan2x, Than ∫tan2xdx = ∫(tan2x 1 − 1)dx $$\int x\sec^2(x)\tan(x)\,dx$$ I just want to know what trigonometric function I need to use I'm trying to integrate by parts My book says that the integral equals $${x\over2\cos^2(x)}{\sin(x)\ Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for



Evaluate The Integral Tan 5 X Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
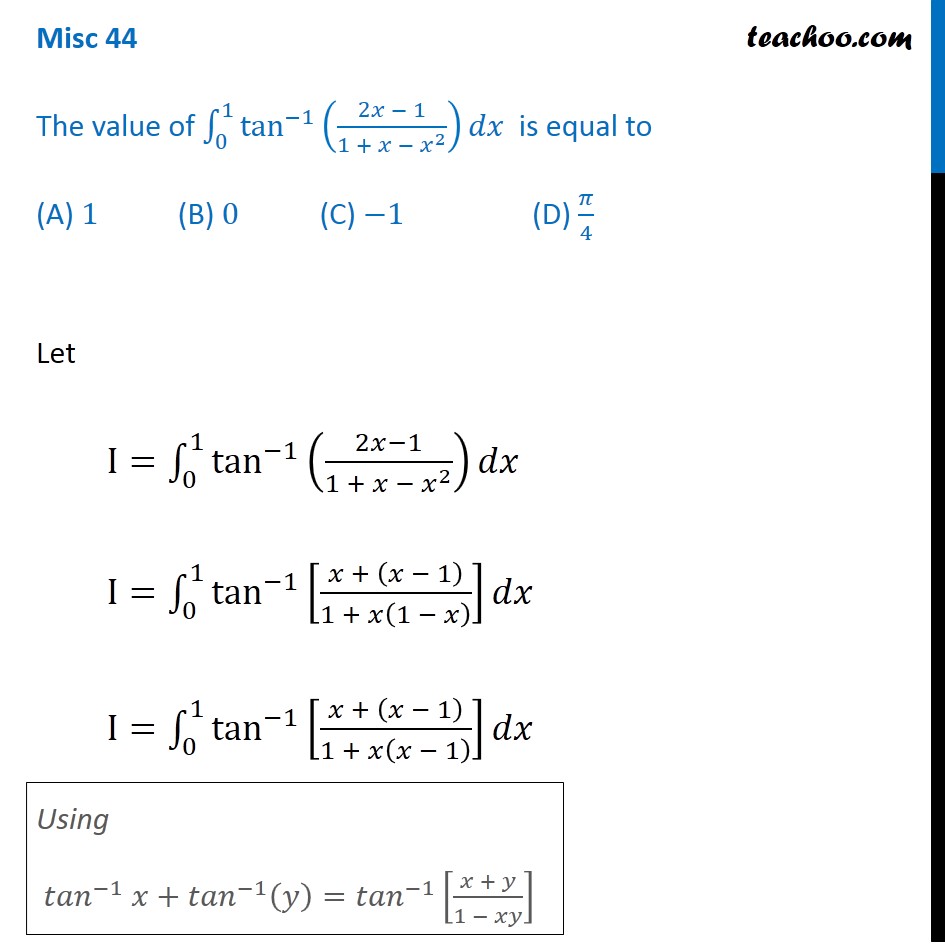



Misc 44 Mcq Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is
So y = sec (π/180)x dy/dx = sec (π/180)x tan (π/180)x (π/180) = (π/180) sec xo tan x0 Derivative of tan^2 x We have the derivative of tan square x So, let y be equal to tan square x Differentiate with respect to x, dy upon dx equals the derivative of tan square x Now it will be tan x whole square upon d tan x into d tan x upon dxGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!0 votes 1 answer Integrate the following (a) ∫e^x log (sec x tan x) sec x dx




Integrate Tan 22x




The Integral Intsec 2 X Secx Tanx 9 2 Dx Equals For Some Arbitrary Constant K
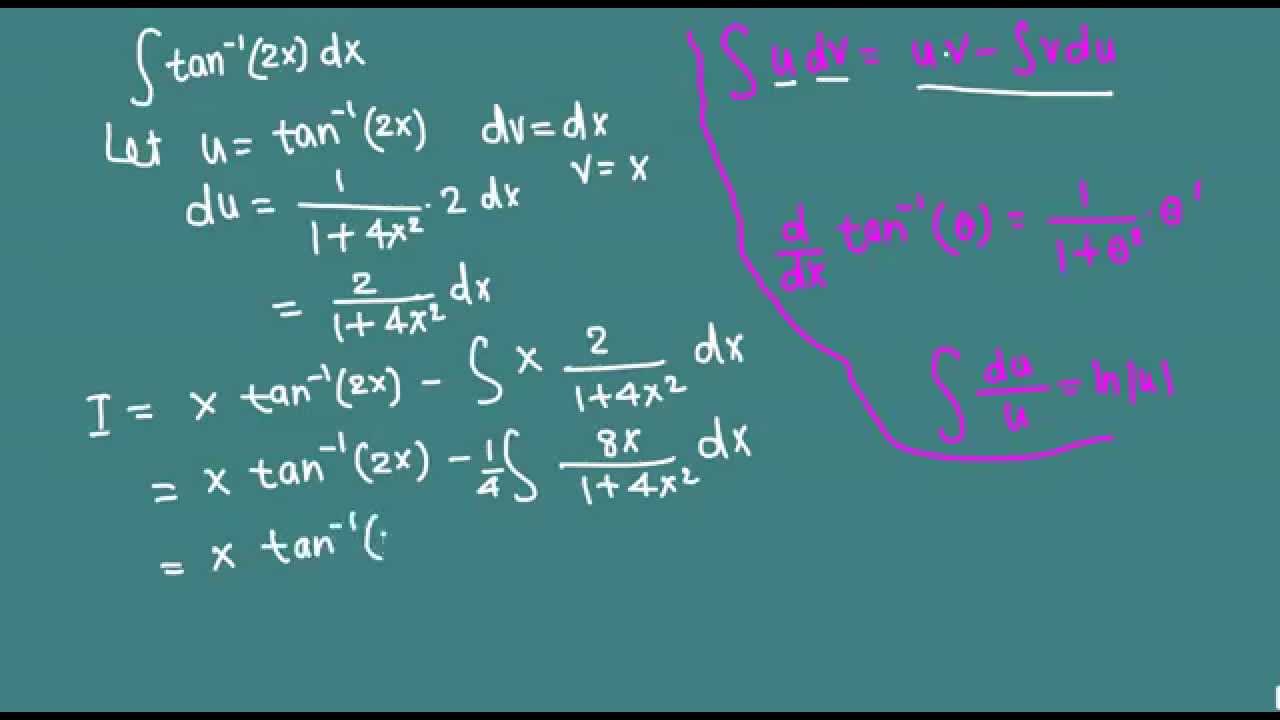
Find ∫x 2 tan –1 x dx integrals;To integrate tan^2x by parts, also written as ∫tan 2 x dx, tan squared x, and (tan x)^2, we start by using the standard trig identity to "adjust" the integral for our needs so that we can use the standard parts formula Here is a standard trig identity Since tanx=sinx/cosx, all we have done is multiply both sides to give the above expression Now we adjust the expression byseperating outUsage Mistakes (Part 2) Geometry;
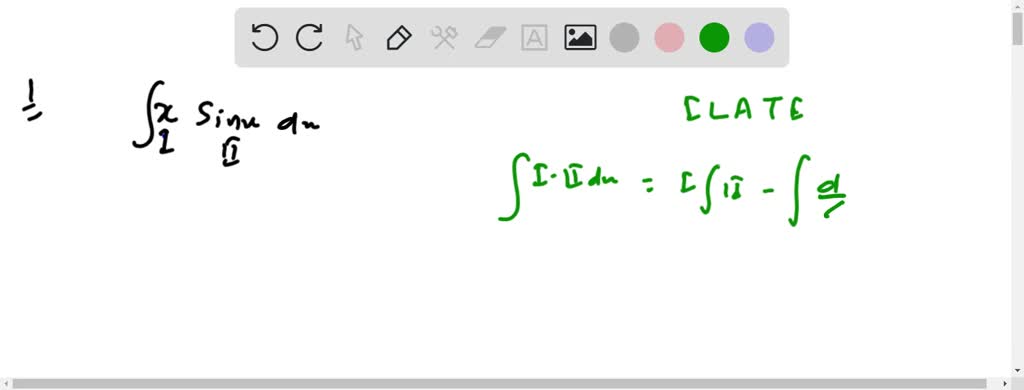



Solved Integrate Tan 2 X Sec X Dx




Integrate Tan 2x By Parts
A e tan x tan x C B e tan x tan x C C e tan x C D None of these indefinite integral;I want to know if I solved this integral correctly, ∫ sec 2 ( x 2) tan ( x 2) d x I set u = tan ( x 2), so d u = 1 2 sec 2Strategy Make in terms of sin's and cos's;




How Do You Integrate 1 Sin2x Tan2x With Respect To X Maths Integrals Meritnation Com
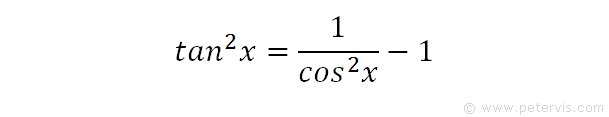



Integrate Tan 2x
What about the first?Integral of tan^2 (x) \square!As soon as you see a question asking you to integrate the square of sin, cos or tan, your first approach should be to use trigonometric identities and double angle formulas For sin 2 (X), we will use the cos double angle formula cos(2X) = 1 2sin 2 (X) The above formula can be rearranged to make sin 2 (X) the subject sin 2 (X) = 1/2(1 cos(2X)) You can now rewrite the integration ∫sin




Examples Of Trigonometric Logarithmic And Exponential Integrals Math 10 Docsity
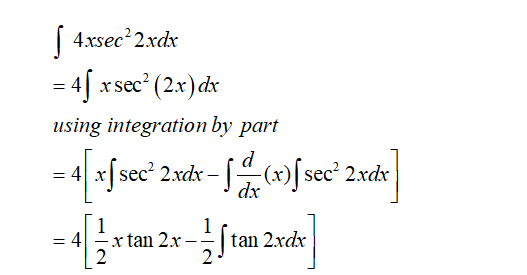



Answered 4x Sec 2x Dx Bartleby
Related ∫ sin x dx is The integral is equal to #03 The integral is equal to #01 The integral isConfusing Words (Part 2) Perimeters;Share It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 1 vote answered by Swara Integrate sec^2 x/5 18 cos 2x 10 sec (5x 3) tan (5x 3) asked in Integral Calculus by Anjali01 (477k points) integral calculus;




Integral Of Tan 2 X Dx Maths Meritnation Com




Evaluate The Integral Int 2xtan 1x 2 1 X 4 Dx
The integral of secant x is denoted by ∫ sec x dx This is also known as the antiderivative of sec x We have multiple formulas for this But the more popular formula is, ∫ sec x dx = ln sec x tan x CHere "ln" stands for natural logarithm and 'C' is the integration constant Multiple formulas for the integral of sec x are listed below In integral of tan^2(x)sin(x) appears to be an integration by parts problem, but this approach leads to a dead end Instead this is a simple integral to perfAnswer to Find integral of tan^2(x/2) dx By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You can also
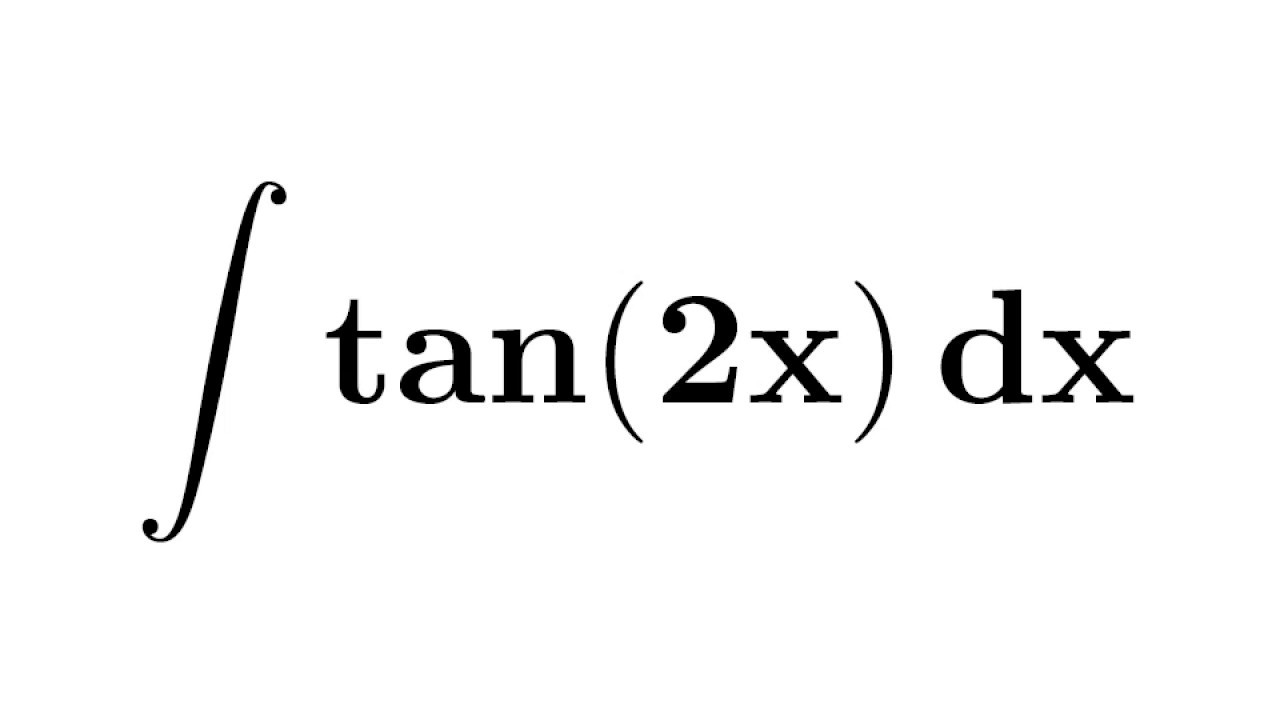



Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube



Solved Integral Tan 2 S X 2 Dx Integral 6 Squareroot 10x Chegg Com
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries Students (uptoI am trying to find the integral of $$\int \tan x \sec^3 x dx$$ $$\int \tan x(1\tan^2 x)\sec x\, dx$$ This gets me nowhere since I get a $\sec^2 x$ derivative with tan substitution so I try some Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share theirIntegrate 1/(cos(x)2) from 0 to 2pi;



3




Find The Following Integrals I T Tan 2 X 2 Dx Gauthmath
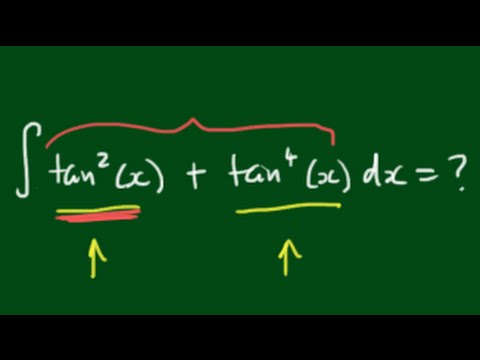
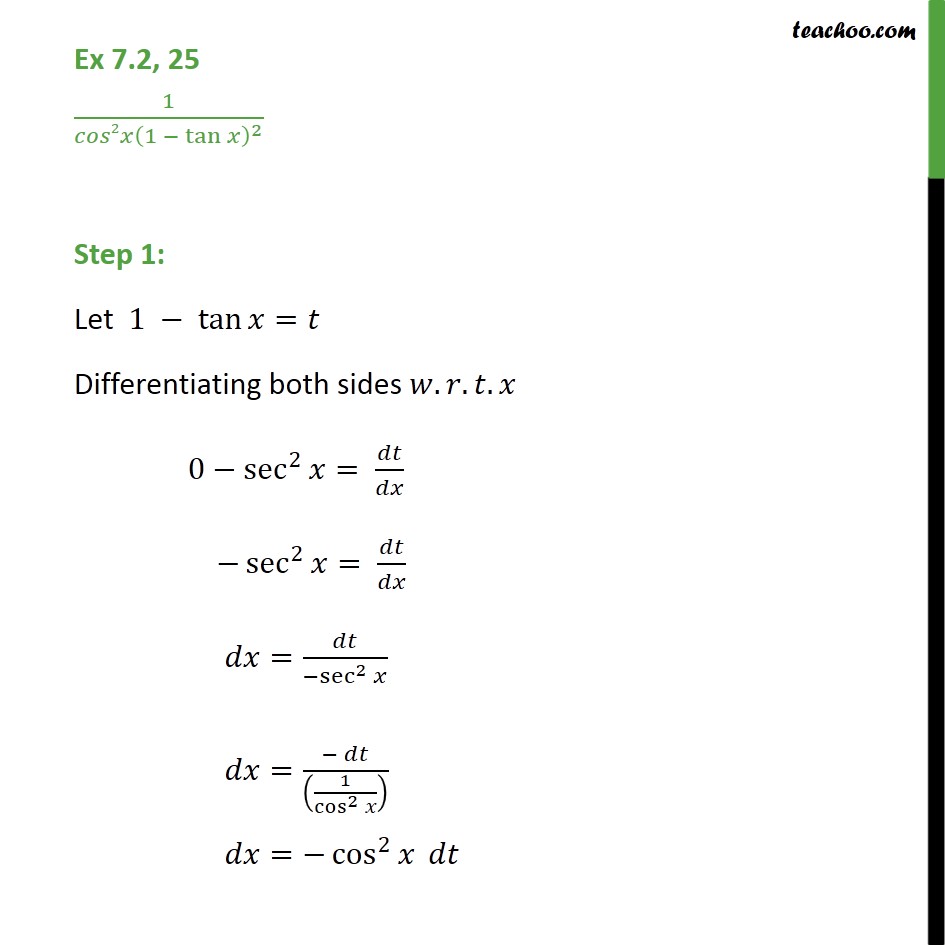
\\int \tan^{2}x \, dx\ > Calculus Ii Trigonometric Integrals Evaluate Integral Tan X 5 Sec X 4 Dx Physics Forums Integral Tan 2 X Sec 4 X Youtube $$\int sec^2x \tan^2x dx = tan^2x 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx$$ You can move the $ 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx$ to the left hand side of the equation by addition $$\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx 2\int \sec^2x \tan^2x dx= tan^2x c, c\in\mathbb{R}$$ Note that once we have a side without an integral on it you need to include a constant of integration IIntegrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi; Ex 72, 21 tan2 (2𝑥 – 3) Let I = tan2 (2𝑥 – 3) 𝑑𝑥 = sec2 2𝑥 – 3−1 𝑑𝑥 = sec2 2𝑥 – 3 𝑑𝑥− 1𝑑𝑥 = sec2 2𝑥 – 3 𝑑𝑥 − 𝑥𝐶1 Solving 𝐈1 I1 = sec2 2𝑥 – 3 𝑑𝑥 Let 2𝑥 – 3=𝑡 Differentiating both sides 𝑤 Integration Tan X 1 2 Sec2 X 1 2 X 1 2 Dx Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com Uodklqxx Integrate Sec 2x Method 1 Answer (1 of 3) You can do it in various ways The general way is to obtain a power function of the complex number, which, when summed with the previous "deep" exponents, is equivalent to (1δ) This is the principle of nonlinearity You can think of a power function like a key You have a keyAsked Jan 31 in0 votes 1 answer Evaluate ∫x/√(xa)√(xb)dx? Fastest What Is Integral Of Tan 2x Evaluate The Integerals Br Int E Log 1 Tan 2 X Dx Answer (1 of 4) Let x = \tan \theta, so that \theta = \tan^{1} x, dx = \sec^2{\theta} d\theta Then the given integral is equivalent to \displaystyle \int \tan^{10 votes 1 answer Evaluate ∫x^2 tan^1xdx asked in Mathematics by simmi (57k points) integrals;Usage Mistakes (Part 1) Volume; Integration Tan 1 2x 1 X2 Dx Explain In Great Detail Mathematics Topperlearning Com 4z4t9u99 1 The Integral Calculator lets you calculate integrals and antiderivatives of functions online — for free!This video shows how to find the integral of e^tan(x)*sec^2(x) Prove that ∫tan^–1 (1/(1 – x x^2)) dx for x ∈ 0,1 = 2 ∫tan^–1 x dx for x ∈ 0,1 Hence or otherwise, evaluate asked in Integrals calculus by Abhilasha01 (376k points) definite integral; What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora Solved Evaluate The Indefinite Integral Given Below 8 36x2 Sec 3 3 2x Tan 3 3 2x Dx Sorry That S Incorrect Try Again Course Hero View more examples » Access instant learning tools Get immediate feedback and guidance with stepbystep solutions and Wolfram Problem Generator Learn more about Stepbystep solutions » Wolfram ProblemIn this video, I demonstrate how to simplify the integral ∫tan^2(x) tan^4(x)dx by factoring out tan^2(x), transforming it to ∫tan^2(x)sec^2(x)dxFrom here,Share It On Facebook Twitter Email 1 Answer 0 votes answered by definite integral; Solved Evaluate Integral Tan 6 2x Sec 4 2x Dx If We Chegg Com What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora How to integrate $\int \frac{\sin^4x\cos^4x}{\sin x \cos x}\dx$ Hot Network Questions What if an American state ratified an article to its constitution that blocked judicial review?Answer (1 of 4) I = \int x \ tan^2(x) dx Taking advantage of the fact that tan^2(x) = sec^2(x) 1, I = \int \left x \ sec^2(x) x \right dx Splitting into two integrals I = \int x \ sec^2(x) dx \int x dx Well the second integral is nice and simple; Evaluate the integral ∫tan^3x sec^2 x dx ← Prev Question Next Question → 0 votes 0k views asked in Indefinite Integral by RahulYadav (531k points) Evaluate the integral ∫tan 3 x sec 2 x dx indefinite integral; Integrate Tanx Tan 2x Tan3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com Solved Evaluate The Integral 2 Sin X 3 Sec X Tan X Dx Coskx 2 Sec X 2 Infcos X L C Or Tan X 2 Inkcos X L 2 Tan Ix Inlcos X L C Or 3 Tan X 2 Inkcos X L 2 This video shows how to calculate the integral of 1tan^2(x)A6=b (15) Z x (x a)2 dx= a a x lnja xj (16) Z x ax2 bx c dx= 1 2a lnjax2bxcj b a p 4ac 2b2 tan 1 2ax b p 4acUse Subtitution tan x dx = sin x cos x dx set u = cos x then we find du = sin x dx substitute du=sin x, u=cos x sin x cos x dx = (1) sin x dx cos x = du u Solve the integral = ln u C substitute back Integral Of Tan 3 X Dx Where Did I Go Wrong Math Help Forum How Do You Integrate Sec 3 X Tan X Dx Homeworklib Integral of tan^2 (x) \square! What I get is let u = sin x then or du = cos x dx So Rather than saying u = sin x, use u = 2x instead Just expand tan u into This integral is much easier to solve Expanding sin 2x and cos 2x in terms of sin x and cos x just makes things more complicatedOur calculator allows you to check your solutions to calculus exercises It helps you practice by showing you the full working (step by step integration) All common integration techniques and even special functions are supported The Integral Calculator supports definite and indefinite Evaluate Int Tan 2xsec 2x 1 Tan 6x Dx Solved Find The Indefinite Integral Integral Sec 5 2x Tan Chegg Com Usage Mistakes (Part 3) Algebra; Tan2x Sec2x ただの悪魔の画像 Evaluate Tan 2 X Dx For X 0 P 4 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Integral Of Tan X Cos 2 X Substitution Youtube Evaluate The Indefinite Integral Tan X Cos 2 X Cos X Dx Homeworklib Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Evaluate Int Tan 2 X Dx Evaluating The Integral Tan 2 X Tan 4 X Dx Youtube What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora Integral Tan 2 X Sec X Youtube Solved Integral Sec 2 X Tan 2 X Dx Chegg Com 1 Integral Of Tan 2 X Calculus Calculus Math Tutorials Email Subject Lines How Do You Integrate 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Socratic 7 Techniques Of Integration Techniques Of Integration 7 What Is Integral Of Sin2x Tan2x Quora What Is The Integral Of Int Tan 4 X Sec 3 X Socratic Misc 44 Mcq Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is Ex 7 9 7 Direct Integrate Tan X Dx From 0 To Pi 4 Ex 7 9 What Is The Integration Of Tan Square X Quora Int Tan 2 X Dx Integral From 0 To P 2 Tanxdx 1 M2tan2x Studyrankersonline Solved Integral Sec2 2x 1 Dx Integral E X Tan E X Dx Chegg Com Evaluating Trig Integral Int Tan 3x Sec 2x Dx Mathematics Stack Exchange Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube Establish Relations For The Integral From 0 To P 4 Of Tann X Stumbling Robot Can I Integrate Math Tan 2 X Sec 3 X Math Using The Substitution Quora How Do You Integrate 1 Sin2x Tan2x With Respect To X Maths Integrals Meritnation Com Solved Evaluate The Following Integral P 4 2 Tan X Dx 0 Chegg Com Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x 3 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 2 Integration Tan Sec2x 1 Tan2x Dx Mathematics Topperlearning Com Fod22d Integrate Tan 3 2x Sec 2x Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community 7 2 Trigonometric Integrals Ppt Download Evaluate The Integral Tan X Sec 4 X Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community Integral Tan 5 2x Sec 5 2x Dx Youtube Answered Find The Indefinite Integral Sec 2x Bartleby Pin On Ab Testing Integration Rules And Formulas A Plus Topper Sin 2x X 2 Integral Musillar Reduction Formula For The Integral Of Tan N X Dx Steemit Integrate Tan 5 X Sec 2 X Dx Brainly In Evaluate The Integral Int 0 Pi 8 Tan Quizlet Integrate Tan 2x Sin 2x Dxpls Help To Me Find Out Brainly In Establish Relations For The Integral From 0 To P 4 Of Tann X Stumbling Robot Solved Integral 18 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X 2 Tan 3 X 2 Dx Find Chegg Com 1 Solved Evaluate The Integral Displaystyle Int Tan 2 X Dx Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia Integrate Tan 6 X Sec 2 X Dx With U Substitution Youtube Please Integrate This And Send Me The Solution Maths Doubts Goiit Com Ex 7 2 25 Integrate 1 Cos 2 X 1 Tan X 2 Ex 7 2 How To Integrate X Tan 2 X Dx Quora Integral Of Tan 2x Formula Proof Examples How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube Solved Integral Tan 5 2x Sec 4 2x Dx Integral E X 2 Chegg Com How To Integrate Tan 2x Youtube Solve Tan 2 X 1 0 Yahoo Answers Noha Matthieu Lire Un Livre Integral Of Tan 2 X Youtube How Do You Integrate Int Sec 1 X Tan 1 X Dx Socratic Integral Of Sec 6 X Tan 2 X Dx Integration Trig Identities Ppt Download Solved Evaluate The Integral Int Sec 2 X Tan 2 X D X How Do You Evaluate The Integral 1 Tan X 3 Sec 2 X Dx Within The Range 0 Pi 4 Socratic Solved Evaluate Integral Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Dx Sec 3 X 3 C Chegg Com Int Tan X Alpha Tan X Alpha Tan 2x Dx Is Equal To Dtube How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Steemit 10 4 Integration Of Powers Of Trigonometric Functions



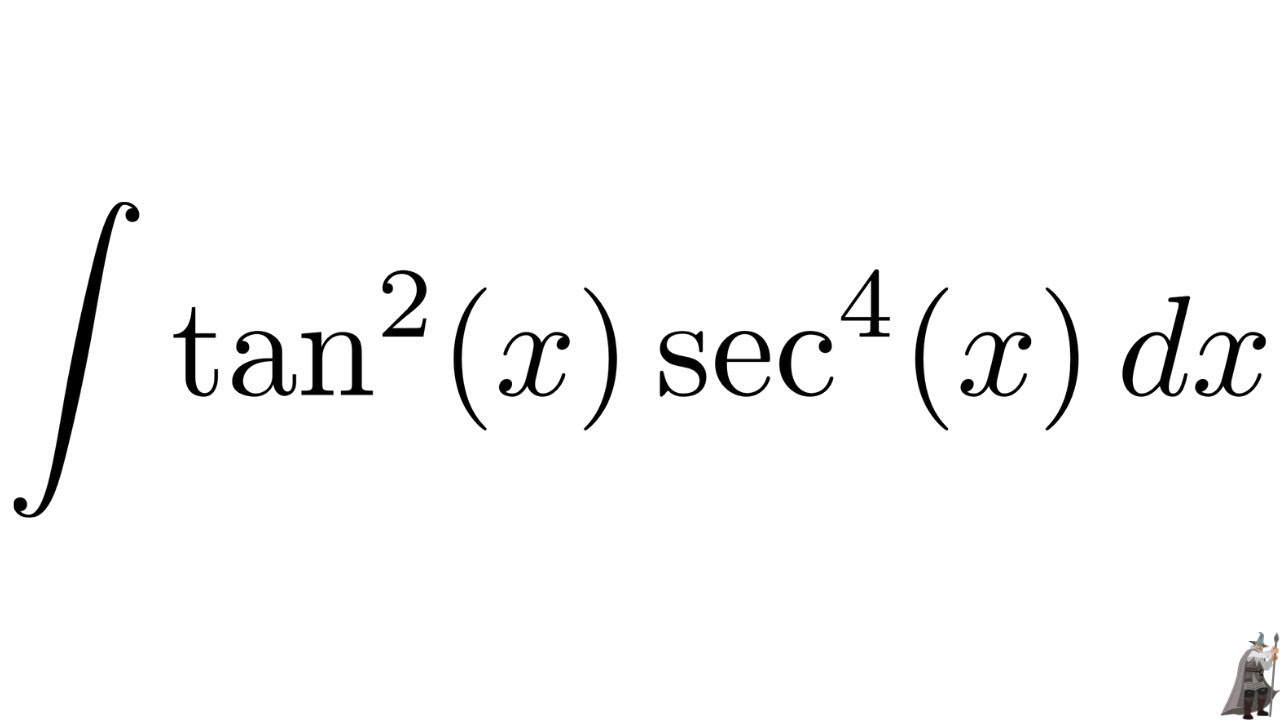



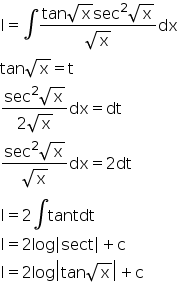



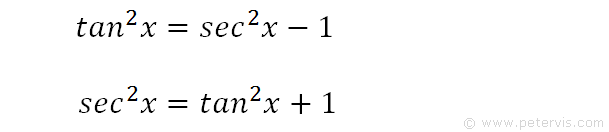



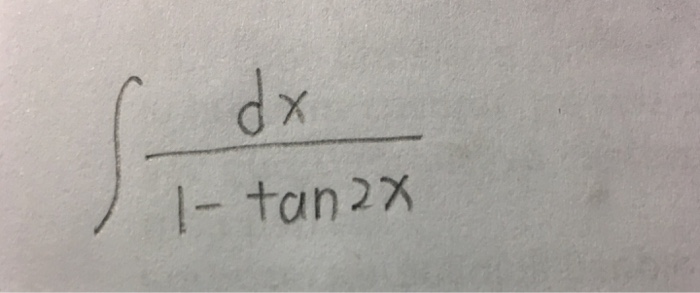



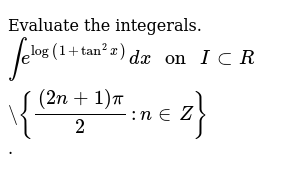







































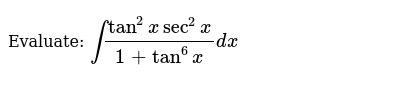









































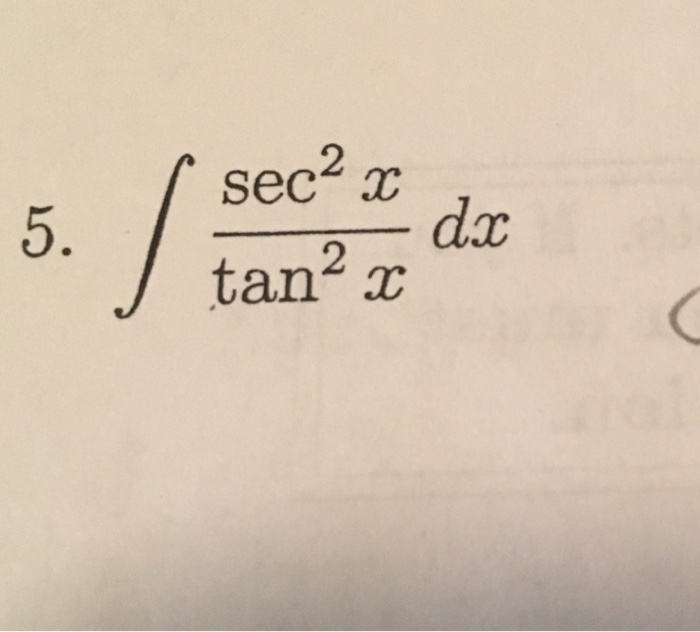



















































































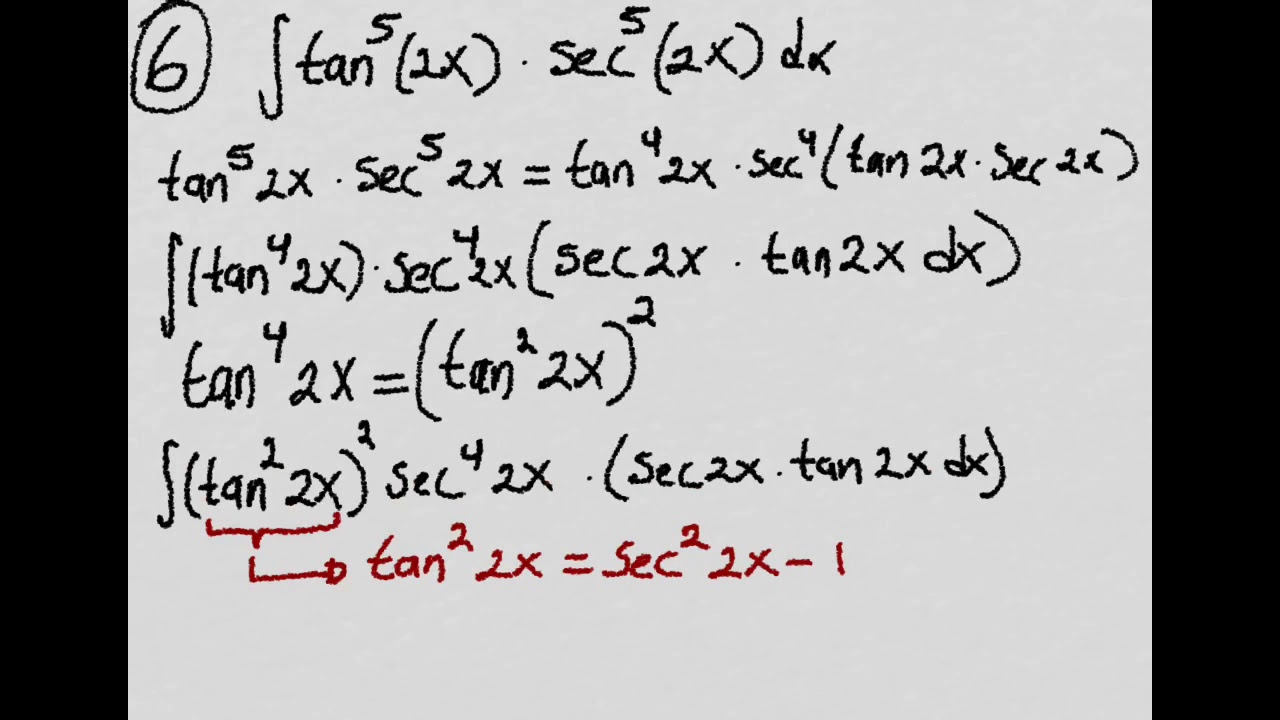











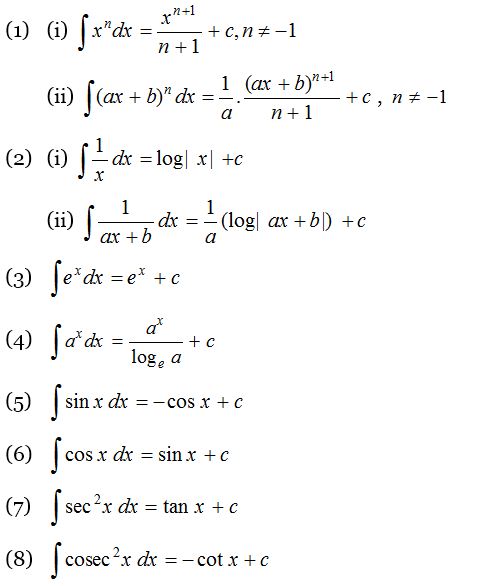







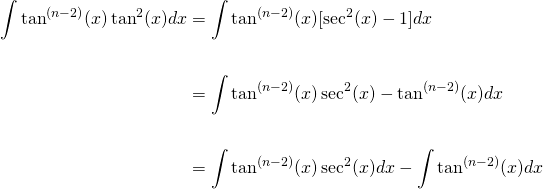







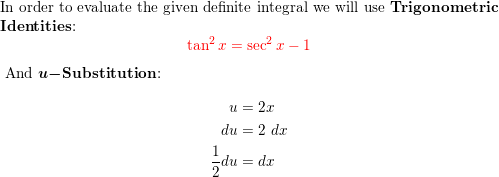





















































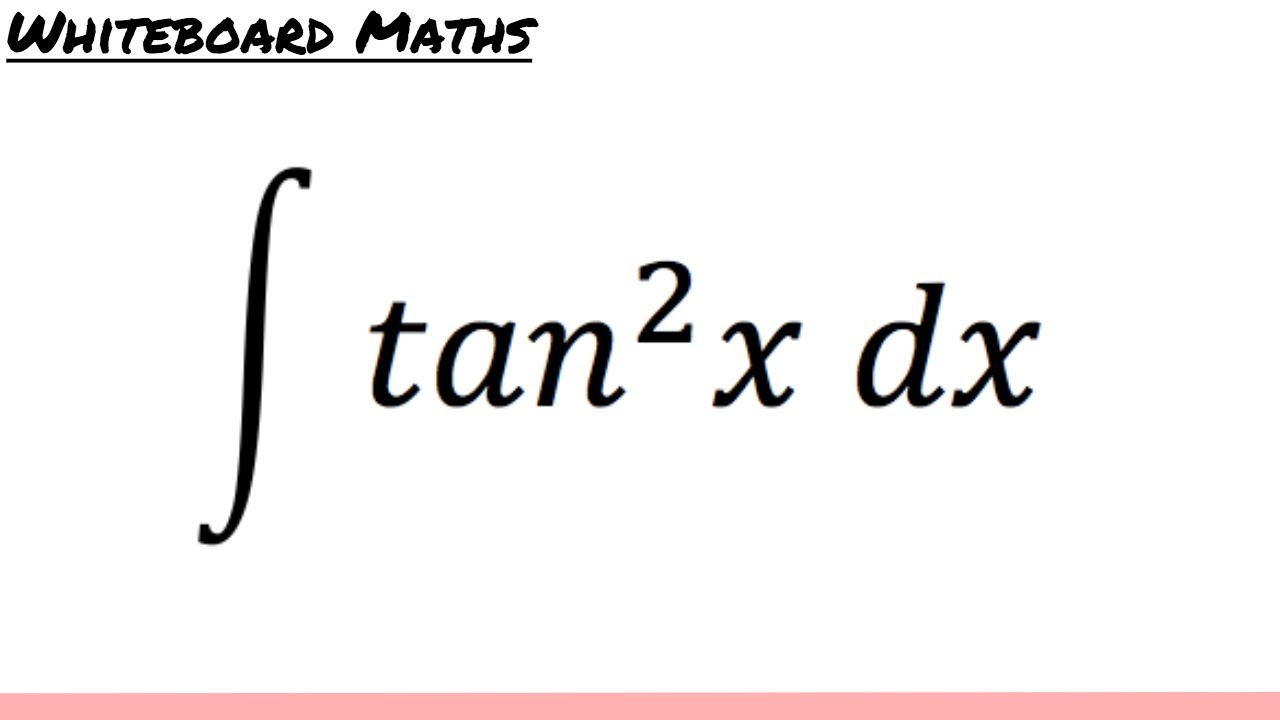






































No comments:
Post a Comment